Cyber Security Basics for Beginners

We may earn a small fee from the companies mentioned in this post.
As our world becomes increasingly connected and reliant on technology, the importance of cyber security cannot be overstated. It is crucial that we equip ourselves with the knowledge and skills to protect our sensitive data and systems from malicious attacks. This includes gaining an understanding of the fundamentals of cybersecurity.
So, are you ready to embark on a journey to understand the world of cyber security and learn the cyber security basics? Let’s dive in…!
A Comprehensive Guide to Cyber Security Basics
Short Summary
Understanding cyber security basics is a critical business concern for organisations of all sizes.
Organisations and individuals should be aware of common cyber attacks and take preventative measures to protect their systems from malicious exploitation.
- Understand the best cyber security topics for beginners that includes netwokring security basics and physcal security
- Protect yourself from cyber threats and network security vulnerabilities
- Understand the types of cybersecurity threats and the controls used to protect organisations
- Cyber security best practices such as strong passwords, two factor authentication, regular software updates, and safe online behaviour are essential for protecting devices & data from potential threats.
Understanding Cyber Security Basics

In today’s interconnected world, cyber security plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety of sensitive data, computer systems, networks, and software applications from cyber attacks. With cyber threats evolving at an alarming pace, it has become an essential business concern for organisations of all sizes.
Cyber security typically consists of various categories, including:
- Network Security: Measures to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data during transmission. Network security solutions include firewalls, anti-virus software, intrusion detection and prevention systems.
- Application Security: Focuses on keeping software and devices free of threats. A compromised application could provide access to the data its designed to protect. Security begins in the design phase, well before a program or device is deployed.
- Endpoint Security: Concerns securing endpoints, or end-user devices like desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. Endpoint security systems protect these devices from being exploited by malicious campaigns and can include antivirus software, email filtering, and web filtering.
- Data Security: Involves protecting data from unauthorized access and data corruption throughout its lifecycle. Data encryption, hashing, tokenization, and key management practices that protect data across all applications and platforms.
- Identity Management: Systems that can ensure only the right people have access to the technology resources. This includes processes and technologies to manage and verify identities and access privileges of users.
- Database and Infrastructure Security: Involves securing the systems that store and manage data. Measures include database activity monitoring, physical security measures, and secure configuration of infrastructure components.
- Cloud Security: Specific to safeguarding cloud computing environments. This can include securing data, applications, and infrastructures involved in cloud computing, including the use of security policies, technologies, controls, and services.
- Disaster Recovery/Business Continuity Planning: Strategies for responding to and recovering from significant cybersecurity incidents that involve data loss or service interruption. This ensures that a business can continue operating and return to normal operations as quickly as possible after a disruption.
Addressing these security risks can be challenging, especially with the rise of remote work and reduced oversight of employees conduct and device security. Moreover, legal requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandate that organisations adopt suitable safeguards to secure personal data.
The Evolution of Cyber Threats
The history of cyber threats, and cyber attacks, can be traced back to the 1980s when the first computer virus emerged. Since then, cyber threats have evolved significantly, with malware such as WannaCry ransomware making headlines around the world.
Cyber threats come in many forms, including cybercrime, cyber-attacks, cyberterrorism, malware, phishing scams, botnet attacks, and cryptocurrency hijacking. These threats can have severe consequences, such as theft of passwords and banking details, reduced system performance, and shortened device lifespan.
This highlights the critical importance of cyber security, which plays a vital role in safeguarding against these threats and ensuring the implementation of data encryption, endpoint security, and employee training and awareness.
You may find this article useful on The 7 Types of Cyber Threats
Key Components of Cyber Security
Cyber security encompasses several key components, including confidentiality, integrity, availability, authentication, authorisation, and non-repudiation. Confidentiality in cyber security refers to measures taken to restrict access to sensitive information, preventing unauthorised individuals such as cyber attackers and hackers from gaining access.
Integrity ensures that data remains consistent, accurate, and reliable throughout its lifetime, preventing unauthorised modifications, deletions, or access during transmission. Availability guarantees that authorised users can access and use data on demand, ensuring that data remains accessible when required.
Authentication, another crucial component of cyber security, is a security process that requires users to provide two distinct authentication factors to confirm their identity.
Authorisation, on the other hand, involves granting access to resources based on a user’s identity, allowing the system to determine what actions a user is authorised to perform. Lastly, non-repudiation is a security measure that ensures a user cannot deny having taken an action, such as sending an email or making a purchase.
These primary components, combined with network security and information security measures, form the backbone of a robust cyber security strategy.
Checkout our informative article on what a cyber attack means
Common Cyber Attacks and How to Prevent Them

Organizations and individuals face a myriad of cyber attacks that exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks. Some common methods used to jeopardise cyber security include gaining control of computer systems through malware, phishing scams, and network vulnerabilities.
These attacks can take various forms, such as password attacks, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, clickjacking, cryptocurrency hijacking, and romance scams. To defend against these malicious attacks, it is crucial to understand each type of threat and implement effective prevention strategies.
Malware Protection
Malware is a type of malicious software designed to damage or exploit programmable devices, services, or networks, causing severe consequences. Therefore, it is essential to use anti-virus and anti-malware programs to minimize a computer’s susceptibility to malware.
It is also crucial to scan external storage devices for possible threats, ensuring they are free of malicious software. Implementing lock-and-erase options, two-factor authentication, and regularly updating software are other effective malware protection measures that can safeguard your devices and data from threats.
Checkout the blog on how to prevent viruses your computer
Defending Against Phishing Scams
Phishing attacks are a common type of email attack where the perpetrator sends an email that appears to be from a legitimate source, but is actually crafted to deceive the recipient into divulging sensitive information, such as login credentials and bank account details.
To defend against phishing scams, it is crucial to verify the source of an email by contacting the sender to confirm its authenticity. Additionally, downloading email attachments should only be done if you are certain of their legitimacy to avoid potential risks.
You may find our blog on protecting yourself from phishing useful
Securing Your Network
Securing your network is of paramount importance for protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access and data breaches. A layered defence strategy, consisting of firewalls and access control measures, helps address potential vulnerabilities in operating systems and network architecture.
The use of strong passwords and regular updates to software are also crucial for maintaining a secure network that incorporates good network security.
Data encryption, a security measure that encodes data so that only authorised users can access it, is another essential component of network security. Having a recovery plan in place ensures that your system can be restored in the event of a security breach or disaster.
Essential Cyber Security Measures for Individuals and Businesses

Various essential cyber security measures can be implemented by individuals and businesses to protect their sensitive data and systems from cyber threats.
Utilising a virtual private network (VPN) can help safeguard data from being intercepted by malicious entities, while also providing access to geo-restricted content. Installing antivirus software protects your computer from malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans.
Furthermore, the use of secure passwords and regular updates to software are crucial for ensuring the safety of your electronic accounts and devices. Lastly, backing up critical data is of utmost importance to ensure that important information is safeguarded in the event of potential loss.
Check out our imformative blog on essential cyber security awareness training
Protecting your data
In the realm of cyber security, it is important to understand the basic concepts of cybersecurity, and few concepts are more important than protecting your data. This is outlined by the CIA Triad, which stands for – confidentiality integrity availability. This triad serves as the cornerstone for cyber security basics and for any effective data security strategy. Understanding its components is crucial for both individuals and organisations aiming to protect their digital assets.
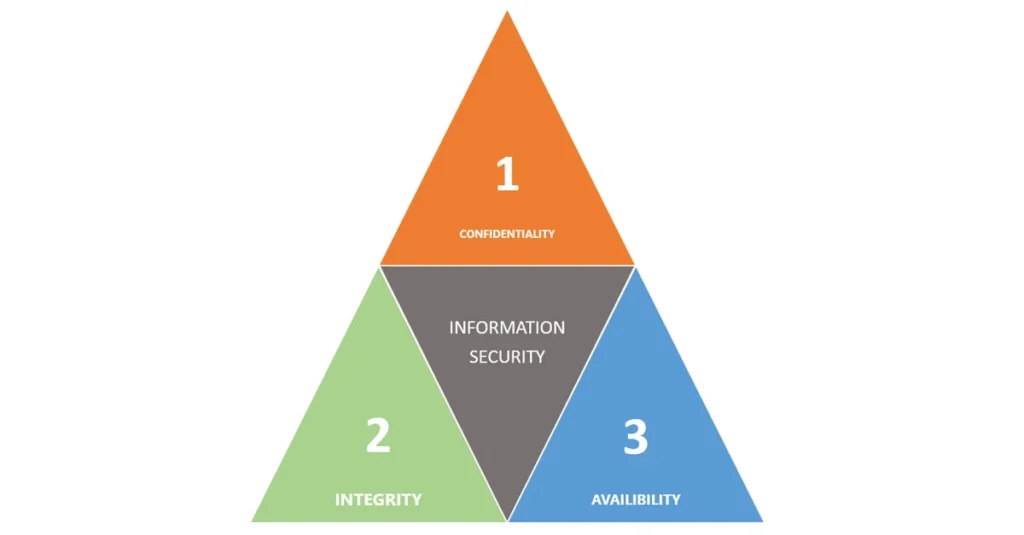
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is all about keeping sensitive information restricted to authorised users only. Imagine your personal details, financial records, or company’s trade secrets falling into the wrong hands. The consequences could range from identity theft to corporate espionage. Employing strong encryption methods and secure authentication protocols are common ways to ensure confidentiality.
Integrity
Integrity ensures that the data is reliable and hasn’t been tampered with. In a world where information is power, the corruption of data can lead to disastrous outcomes. For example, altered medical records could result in incorrect treatments, while manipulated financial data could lead to fraudulent activities. Hashing algorithms and digital signatures are tools commonly used to maintain data integrity.
Availability
The last pillar, Availability, ensures that data and systems are accessible to authorised users when they need it. Downtime can be costly and, in some cases, life-threatening. Imagine a hospital where patient records are unavailable, or a financial institution where transaction data is inaccessible. Ensuring robust network architecture and implementing backup systems are key to maintaining availability.
The CIA Triad is not just a theoretical concept but a practical framework that underpins effective data security strategies and is an integral component to cybersecurity best practices. By giving due attention to Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, you’re setting a strong foundation for safeguarding your digital assets against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. So, the next time you think about the cyber security basics, remember the CIA Triad, as it’s the basic yet powerful principle that keeps our digital world secure.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a crucial measure for protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access and forms an essential element of the basics of cybersecurity. It involves converting plain text into a coded message that can only be read by authorised parties, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure.
The encryption process involves converting plain text into codes using an encryption algorithm, referred to as ciphertext, which is then transformed back into plain text through decryption. The importance of data encryption cannot be overstated, as it provides an additional layer of security that safeguards sensitive information from unauthorised access.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is a critical component of cyber security, as it protects devices like desktops, laptops, mobile phones, and tablets from malicious threats and cyber attacks. Strategies employed for endpoint security consist of host based firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption, while hardware used for endpoint security comprises routers, switches, and access points.
Endpoint security provides protection from malicious code and unauthorised access, helping to prevent data breaches, a cyber attack and other security incidents. Implementing regular software updates, utilising strong passwords and two-factor authentication, and adhering to safe online practices are all highly recommended for ensuring robust endpoint security.
Employee Training and Awareness
Employee training and awareness play a vital role in reducing the risk of cyber attacks. Educating employees on how to recognize, avert, and address cyber threats through consistent training and educational programs is essential for fostering a culture of cyber security.
Implementing policies that ensure the use of strong passwords, enforce payment card security, and require regular backups of critical data can also contribute to the security of sensitive information. By providing employees with the knowledge and tools they need to protect their digital environment, organisations can significantly reduce the likelihood of cyber attacks and security breaches.
Roles and Responsibilities in Cyber Security
In the field of cyber security, there are various roles and responsibilities that contribute to the protection of sensitive data and systems. Leadership commitment is essential for cyber resilience, as it ensures the implementation and enforcement of effective processes.
Ethical hackers, who possess the expertise and capabilities to identify security vulnerabilities and provide advice on cyber attack prevention, are highly valued assets to organisations.
Additionally, intermediate to advanced certifications, such as CISM and CISA, play a crucial role in the information security domain.
Cyber Security Analyst
A cyber security analyst is responsible for conducting analysis and assessments of security risks and vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks, as well as devising and executing security measures to safeguard against these risks. Typically, they hold a degree in cyber security, computer science, information and communication technology, or a related field.
A cyber security analyst’s duties include planning, implementing, and upgrading security measures, conducting security audits, vulnerability testing, and risk analyses, managing networks, and training colleagues.
Ethical Hacker
Ethical hackers, also known as white hat hackers, penetration testers, or red teams, use their hacking skills for lawful and ethical purposes, such as identifying potential security vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks. The intent of ethical hacking is to identify potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited by malicious actors, ensuring that organisations can address these risks proactively.
The Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) certification is a widely recognised credential in the field of ethical hacking, demonstrating an individual’s expertise and commitment to ethical hacking practices. To succeed as an ethical hacker, you should stay abreast of the latest security trends, advocate strong passwords and two-factor authentication, and ensure software is regularly updated.
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
A Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is a senior executive responsible for the security of an organisation’s information and technology assets. The role of a CISO is to ensure alignment between cyber security plans and business operations, as well as the development of appropriate security processes.
A CISO may develop and implement security policies, create security awareness programs, and conduct regular security audits as part of their responsibilities. By aligning cyber security strategies with business objectives and fostering a culture of security awareness, CISOs play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and systems from cyber threats.
Cyber Security Best Practices and Tips
Adopting cyber security best practices and tips can significantly improve the safety and security of your digital environment. Proper password management, for instance, is essential for ensuring that employees create strong passwords and maintain their security. Being cautious when clicking on links can also help prevent deceptive links from leading to malicious websites or downloads.

Regularly updating software is another crucial practice, as it ensures the installation of the latest security patches and protection from the most recent threats. Ultimately, upgrading your IT security systems may be a more cost-effective solution than dealing with the financial repercussions of a security breach.
Check out our informative blog on the best motorhome SatNav
Regular Software Updates
Regular software updates are crucial for maintaining the safety and security of your devices and systems. These updates offer enhanced security, bug fixes, and access to new features, ensuring that your software is performing at its best.
To ensure regular software updates are installed, you can choose between manual or automatic updates. Manual updates require the user to check for updates and install them manually, whereas automatic updates are installed automatically by the software. Maintaining software updates is not only beneficial for security, but also guarantees access to the latest features and bug fixes.
Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication
Utilising strong passwords and two-factor authentication is essential for securing electronic accounts and devices from unauthorised access. Strong passwords, which are intricate and difficult to guess, provide increased protection against cyber threats and hackers.
Two-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security by requiring a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to a mobile device, prior to granting access to an account. When constructing a secure password, it is essential to incorporate a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, as well as using a different password for each account.
You may find our blog on How to Create Good Passwords useful
Safe Online Behaviour
Practicing safe online behaviour is essential for protecting yourself sensitive data and devices from cyber threats. This includes respecting others, refraining from engaging in drama, being respectful, disagreeing politely, safeguarding personal information, avoiding dubious links and downloads, utilising robust passwords, and being cognisant of potential online hazards.
Moreover, disabling Bluetooth when not in use can help prevent hackers from accessing private information. Deleting ads, a type of software that collects information about the user and serves targeted ads, can also enhance your online security.
Lastly, upgrading your security systems by installing the latest security patches, employing two-factor authentication, and using a secure password manager can further bolster your digital safety.
Conclusion – Cyber Security Basics
In conclusion, understanding and implementing cyber security measures are essential in today’s interconnected world.
By familiarising yourself with common cyber threats, adopting essential security measures, recognising the roles and responsibilities in the cyber security field, and practicing safe online behaviour, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks and data breaches.
Understanding the cyber security basics can also be considered essential, reading the articles within this website will enhance your knowledge
Remember, the key to a secure digital life lies in staying informed, vigilant, and proactive in safeguarding your sensitive data and systems. So, take action today and make cyber security a priority in your personal and professional life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cyber security basics for beginners
Cyber security basics for beginners refer to the fundamental principles and practices to protect computers, networks, and data from unauthorised access or attacks. This includes using strong passwords, keeping software up to date, being cautious with email attachments and links, and employing basic network security measures like firewalls and antivirus software.
What exactly does cyber security do?
Cyber security is the practice of protecting computer networks, systems, and programs from digital attacks. These attacks are usually aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information, extorting money from users, or interrupting normal business processes.
How do I learn cyber security skills?
You can learn cyber security skills through various means, including online courses, tutorials, certifications, or university programs. . Joining cyber security forums, attending workshops, and practicing with hands-on labs and tools can also enhance your skills. It’s essential to stay updated with the latest trends and threats by reading blogs, articles, and following industry experts like Jon Cosson.
What does a cyber security professional do?
Cyber security professionals work to identify and defend against cyber threats through a combination of technical solutions, such as firewalls and encryption, as well as educating users on best practices to keep their data secure.
What is the basics of cyber security?
The basics of cyber security involve implementing measures to protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorised access, use, disclosure, disruption, or destruction. This includes practices such as using strong passwords, regularly updating software and systems, enabling firewalls and antivirus software, implementing encryption, conducting regular backups, and educating users about potential threats and safe online practices.
What are the 3 elements of cyber security?
The 3 elements of cybersecurity are:
1. Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive information and ensuring that only authorised individuals have access to it.
2. Integrity: Ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and trustworthy, and preventing unauthorised modifications or tampering.
3. Availability: Ensuring that data and systems are accessible and operational when needed, and protecting against disruptions or downtime.
Cybersecurity describe the basic concepts?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorised access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It involves implementing measures to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats and attacks. Basic concepts in cybersecurity include:
1. Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to authorised individuals or systems.
2. Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy, consistency, and trustworthiness of data and systems.
3. Availability: Ensuring that systems and resources are accessible and usable when needed.
4. Authentication: Verifying the identity of users or systems to ensure authorised access.
5. Authorisation: Granting or restricting access to resources based on user privileges or roles.
6. Encryption: Protecting data by converting it into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms.
7. Firewalls: Network security devices that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
8. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Tools that detect and respond to unauthorized access attempts or malicious activities.
9. Vulnerability Assessment: Assessing and identifying weaknesses or vulnerabilities in systems or networks.
10. Incident Response: A structured approach to addressing and managing security incidents, including investigating, containing, and recovering from cyber attacks.
Remember to consult with cybersecurity professionals for comprehensive guidance and implementation of these concepts according to your specific requirements.
What is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and digital data from unauthorised access, theft, damage, or disruption. It involves implementing measures to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats, such as malware, hacking, phishing, and data breaches. Effective cybersecurity measures include using strong passwords, regularly updating software, implementing firewalls and antivirus software, encrypting sensitive data, and educating users about safe online practices.
What are the five 5 basic principles of cyber security?
Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive information is accessed only by authorised individuals and is protected from unauthorized access.
Integrity: Guaranteeing that data is accurate, reliable, and has not been tampered with or altered by unauthorized individuals.
Availability: Ensuring that information and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed, without significant delay.
Accountability: Keeping individuals accountable for their actions when using or managing data. This involves tracking user activities and implementing controls to ensure actions can be attributed to the responsible party.
Non-Repudiation: Ensuring that a party in a communication cannot deny the authenticity of their signature on a document or the sending of a message that they originated.
Useful external resources
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Cybersecurity Framework – The NIST website is a great resource for tips on basic cyber security practices for individuals, small businesses, and large corporations.
- The National Cyber Security Centre – The NCSC is the UK Governments primary source of information for UK citizens, it includes a significant amount of easy to read guides.
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency’s (CISA) Cyber Essentials – This resource from CISA provides fundamental insights into managing cyber security risks for businesses of all sizes.
With over three decades of experience in the heart of London’s financial sector, I have dedicated my career to the pursuit of robust cybersecurity practices and IT leadership. As a Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), Certified Chief Information Security Officer (C|CISO), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI), I bring a wealth of knowledge and expertise to the table.
My journey in the field of cybersecurity has not only been about personal growth but also about sharing my insights with others. As an international speaker, I have had the privilege of addressing audiences worldwide, discussing the importance of cybersecurity in today’s digital age. My passion for knowledge sharing extends to my work as an author and blogger, where I delve into the complexities of cybersecurity, offering practical advice and thought leadership.
In my role as a CISO and Head of IT, I have overseen the development and implementation of comprehensive information security and IT strategies. My focus has always been on creating resilient systems capable of withstanding the evolving landscape of cyber threats.
My Master’s degree in Cybersecurity has provided a solid academic foundation, which, when combined with my practical experience, allows me to approach cybersecurity from a holistic perspective.
I am always open to connecting with other professionals in the field, sharing knowledge, and exploring new opportunities. Let’s secure the digital world together.